Health
Adenoidid: Complete Guide to Symptoms, Causes, and Effective Treatments
Introduction
Breathing problems, frequent colds, and constant mouth breathing can be worrying—especially in children. One often-overlooked cause behind these issues is adenoidid, a condition linked to inflammation of the adenoids. Many parents and adults search for clear, reliable information but find medical explanations confusing or overwhelming. This guide simplifies everything you need to know, from early symptoms to treatment options, using easy language while staying medically accurate. Whether you’re a parent, caregiver, or someone experiencing persistent nasal problems, this article will help you understand the condition and take informed next steps.
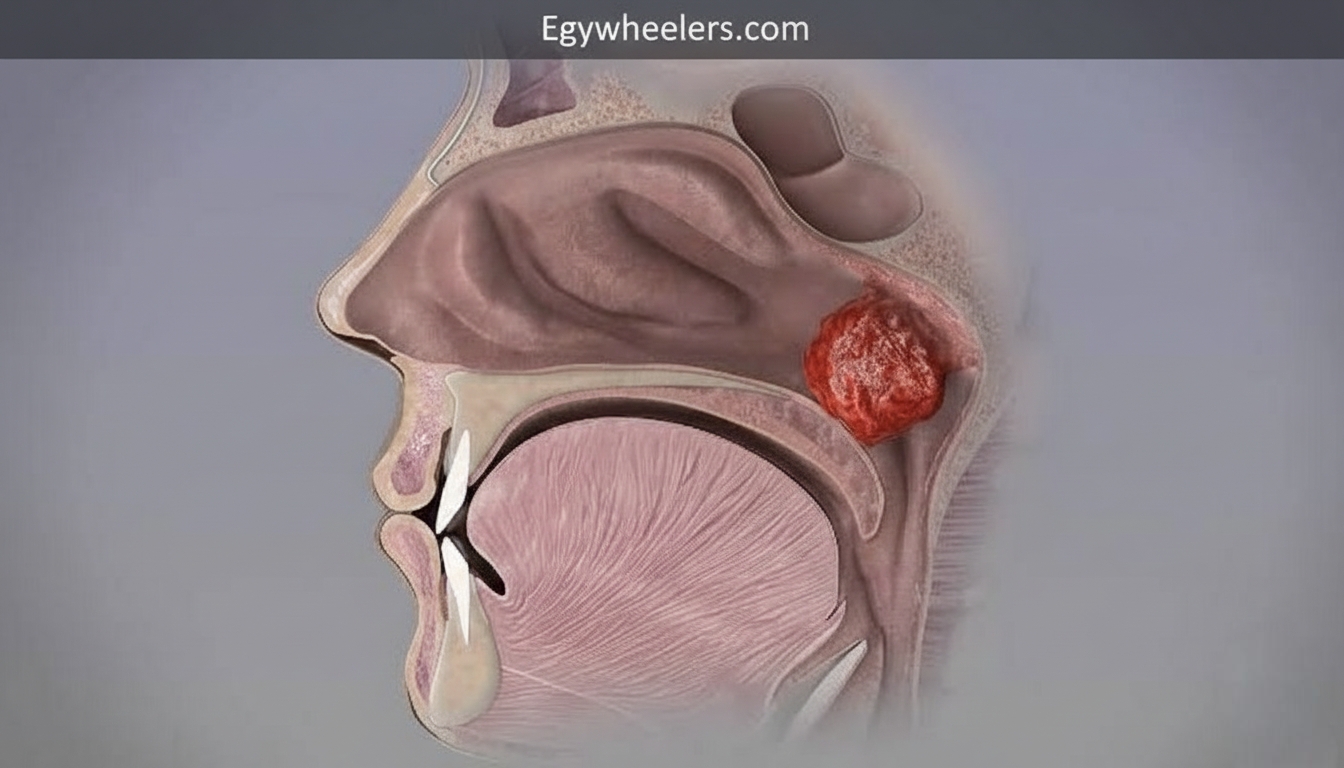
What Is Adenoidid?
Adenoidid refers to inflammation or infection of the adenoids, which are small glands located behind the nose at the roof of the mouth. These glands play a role in immune defense, especially during early childhood, by trapping germs that enter through the nose. When they become swollen or infected repeatedly, breathing and overall health can be affected. Adenoidid is more common in children because adenoids are largest during early years and gradually shrink with age. Adults can experience it too, but it is less frequent. Early awareness helps prevent complications like chronic ear or sinus infections.
Will You Check This Article: The Rowdy Oxford Lawsuit and Its Legal Ripple Effects
Causes and Risk Factors of Adenoidid
The most common cause of adenoidid is repeated exposure to infections, especially viral or bacterial upper respiratory illnesses. Children who attend daycare or school are more exposed to germs, increasing their risk. Allergies can also irritate the nasal passages and contribute to ongoing inflammation. Environmental factors like air pollution, cigarette smoke, and poor indoor air quality may worsen symptoms. A weak immune system or untreated nasal infections can allow the condition to persist. Understanding these triggers helps families reduce risks through hygiene, allergy control, and timely medical care.
Common Symptoms You Should Not Ignore
Symptoms of adenoidid often develop gradually and may be mistaken for frequent colds. Common signs include persistent nasal congestion, mouth breathing, loud snoring, and disturbed sleep. Children may have a nasal-sounding voice or difficulty hearing due to fluid buildup in the ears. Recurrent ear infections and sinus infections are also warning signs. In some cases, poor sleep caused by blocked airways can lead to daytime tiredness, irritability, and trouble focusing. Recognizing these symptoms early allows for faster diagnosis and more effective treatment.
Symptoms in Children vs. Adults
In children, symptoms are usually more obvious because enlarged adenoids block smaller airways. Adults may experience chronic nasal blockage or sinus pressure instead. While children often snore loudly or wet the bed due to sleep disruption, adults may complain of headaches and persistent throat irritation. Knowing the age-specific signs helps doctors choose the right evaluation and care plan.
How Adenoidid Is Diagnosed
Doctors usually diagnose adenoidid through a combination of medical history, symptom review, and physical examination. An ear, nose, and throat (ENT) specialist may examine the nasal passages using a small mirror or flexible camera. Imaging tests like X-rays are sometimes used to assess adenoid size. Hearing tests may be recommended if ear infections are frequent. Accurate diagnosis is important because symptoms can overlap with allergies or sinusitis. A proper evaluation ensures that treatment targets the real cause rather than just masking symptoms.
Treatment Options for Adenoidid
Treatment depends on symptom severity and how often infections occur. Mild cases may improve with medications such as nasal saline sprays, allergy management, or short-term antibiotics if a bacterial infection is present. Doctors may also recommend nasal corticosteroid sprays to reduce swelling. When symptoms are severe or persistent, surgical removal of the adenoids, known as adenoidectomy, may be advised. This procedure is common, safe, and often brings quick relief. Choosing the right treatment improves breathing, sleep quality, and overall well-being.
Medical vs. Surgical Management
Medical treatment is usually tried first, especially in younger children. Surgery is considered when conservative care fails or complications develop. ENT specialists guide families through risks and benefits so decisions are made confidently.
Home Care and Prevention Tips
Good home care can reduce the impact of adenoidid and lower the chance of recurrence. Encouraging regular handwashing helps limit infections. Keeping indoor air clean with proper ventilation and avoiding smoke exposure protects nasal tissues. Managing allergies with doctor-approved treatments reduces chronic irritation. Adequate sleep, balanced nutrition, and hydration support immune health. Regular checkups ensure symptoms are monitored before they worsen. Prevention is not always possible, but these steps can significantly improve comfort and long-term outcomes.
Long-Term Outlook and Possible Complications
With proper treatment, most people recover fully from adenoidid without lasting issues. Untreated cases, however, may lead to complications such as chronic ear infections, hearing difficulties, or dental problems caused by prolonged mouth breathing. Sleep-disordered breathing can also affect growth and learning in children. The good news is that early diagnosis and appropriate care greatly reduce these risks. Working closely with healthcare providers ensures healthy development and lasting relief from symptoms.
Conclusion
Adenoidid may seem like a small issue at first, but its effects on breathing, sleep, and overall health can be significant if ignored. Understanding the causes, recognizing symptoms early, and seeking proper medical advice make a big difference. With today’s effective treatments and preventive strategies, most patients—especially children—experience excellent outcomes. If persistent nasal or breathing problems are affecting daily life, professional evaluation is the best step toward lasting comfort and peace of mind.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Is adenoidid a serious condition?
Adenoidid is usually not dangerous, but untreated cases can lead to complications like ear infections, sleep problems, and hearing issues. Early treatment helps prevent long-term effects and improves quality of life.
2. At what age is adenoidid most common?
It is most common in children between ages 2 and 8 because adenoids are larger and more active during early childhood. The condition becomes less common as adenoids shrink with age.
3. Can adenoidid go away on its own?
Mild cases may improve as a child grows or with basic medical treatment. Persistent or severe cases often require targeted therapy or surgical intervention for full relief.
4. Does adenoid removal affect immunity?
No, removing the adenoids does not weaken the immune system. The body has many other tissues that continue to protect against infections effectively.
5. When should I see a doctor?
You should see a doctor if symptoms like chronic nasal blockage, snoring, or repeated ear infections last more than a few weeks or interfere with sleep and daily activities.
